Multi-Perspective Enterprise Modelling (MEMO)
Motivation
Planning, designing, introducing, and maintaining corporate information systems is a complex endeavour. Beyond demanding a deep understanding of a company's current situation, it has to be remembered that introducing advanced information technology has to allow for new ways of organizing the business. It is an aspect emphatically stressed by the numerous authors who recommend "business redesign" or "business process redesign". Like system design, analyzing and redesigning a corporate strategy and a company's organisation respectively are complex tasks on their own. Management Science and organizational theory offer a wide range of dedicated approaches for analyzing and shaping a firm's strategy as well as for organizational (re)design. Often they are based on graphical models which are introduced to illustrate essential concepts and interrelations - and to communicate them to others who should be involved. Organizational models cover a wide range from rather prosaic to more formal representations. This is similar to models for strategic planning. They usually stress a more abstract view with highly aggregated data. Strategic and organizational models are usually based on different concepts. Furthermore, they generally have nothing in common with conceptual models used in software engineering. While there is certainly need for specialization, such a separation of concerns can be seen as a major inhibitor of efficient information systems. Enterprise models are aimed at providing a medium to foster discourses between people with different professional backgrounds. At the same time they serve as a conceptual basis of highly integrated information systems.
Concepts
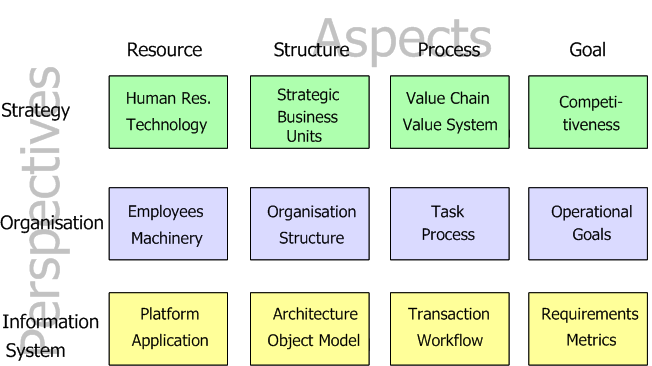
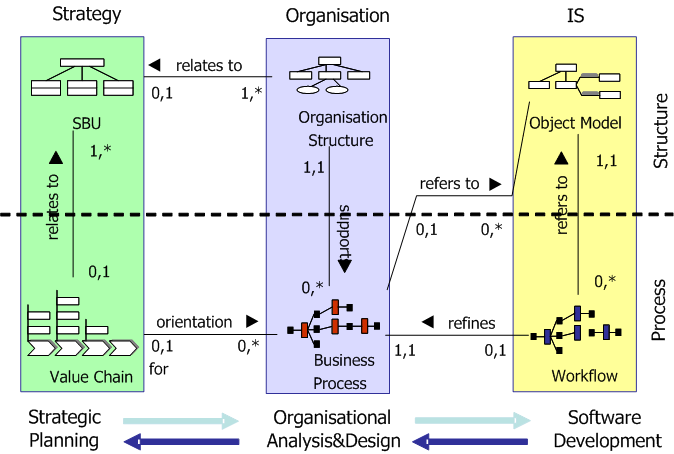
To support the development of powerful enterprise models, MEMO offers a framework that allows structuring an enterprise to a high degree of abstraction. It corresponds to abstractions common in management science and software engineering. The framework suggests three main perspectives on the enterprise: strategic, organizational, and via the information system. The perspectives themselves are further detailed by different aspects (resource, structure, process, and goal). For instance, business process models would be assigned to the perspective "organisation" and the aspect "process". To support conceptual models that are semantically rich and intuitive, MEMO includes an extensible set of specialized modelling languages. The modelling languages are defined within a multi-layer language architecture.
Macro Process
Our work in Philosophy of Science is mainly inspired by the question whether research goals and methods of the information systems discipline are essentially different from those of the neighbour discpilines. We found that informations systems research is essentially different in one respect which is clearly expressed by an approach that we call "constructivist" (sometimes referred to as "design science"). It recommends to construct reality by introducing new ways of coordinating cooperative work. Where the inductivist approach assumes that the variance in using information and expressing it through languages is a necessary reflection of the variety of tasks to be taken into account, the constructivist approach relies on the presumption that variance in actual information use and related coordination mechanisms is the result of an - at least partially - arbitrary process. For this reason, reducing variance by introducing new common concepts to handle information would not necessarily cause dysfunctional effects. Moreover, if the processes they are to be used in were thoroughly designed, they would contribute to more efficiency. In any case, those common artefacts would allow for a high level of integration and reusability.
Despite the prospects of the constructivist approach, it bears a severe epistemological problem: In order to allow for a rational growth of knowledge we need criteria to comparatively evaluate competing constructions. Usually, these artefacts, like models and modelling languages, cannot be validated against reality in a straightforward fashion. We have worked on methods to evaluate artefacts (especially modelling languages and conceptual models). Other work includes reflections upon the appropriate language for information systems research, methods of empirical research and the relationship between theory and praxis.
- Reference Business Processes and Strategies for E-Commerce (ECOMOD)
- Middleware platform for mobile enterprise solutions (Mobilo)
- Flottenmanagement im Handwerk (FlottHIT)
- Project management in crafts businesses through ITg (ProHIT)
- Enterprise Modelling and Performance Optimisation (EMPOSME)
- Enterprise IT Management Modelling Language (EITM-ML)
- Enterprise Modelling Software Tool for Applying the MEMO Method (MEMOCenterNG)
- Hospital Engineering - Innovative Pathways for Hospitals of the Future (HospEngineering)
- Implementing selected languages of MEMO using ADOxx (MEMO4ADO)
- EMSca Enterprise Model (EMSCa)
- Language Engineering for Multilevel Modelling (LE4MM)
Please note that this section only displays current staff. If you are looking for contact data from former staff, please go to the respective section.
- Bock, Alexander; Frank, Ulrich: MEMO GoalML: A Context-Enriched Modeling Language To Support Reflective Organizational Goal Planning and Decision Processes. In: Comyn-Wattiau, Isabelle; Tanaka, Katsumi; Song, Il-Yeol; Yamamoto, Shuichiro; Saeki, Motoshi (Ed.): 35th International Conference on Conceptual Modeling (ER 2016). Springer, 2016, p. 515-529. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-46397-1_40 Details Full textCitation
- Bock, Alexander; Frank, Ulrich: Multi-Perspective Enterprise Modelling – Conceptual Foundation and Implementation with ADOxx. In: Karagiannis, Dimitris; Mayr, Heinrich C.; Mylopoulos, John (Ed.): Domain-Specific Conceptual Modeling – Concepts, Methods and Tools. 2016, p. 241-267. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39417-6_11 Details Full textCitation
- Heß, Michael; Kaczmarek, Monika; Frank, Ulrich; Podleska, Lars; Taeger, Georg: Towards a DSML for Clinical Pathways in the Realm of Multi-Perspective Hospital Modelling. In: Becker, Jörg; Vom Brocke, Jan; Marco, Marco de (Ed.): Proceedings of the 23rd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2015). Münster, 2015. doi:10.18151/7217355 Details Full textCitation
- Goldstein, Anat; Frank, Ulrich: Components of a multi-perspective modeling method for designing and managing IT security systems.. In: Information Systems and e-Business Management (2016), No 14, p. 101-140. doi:10.1007/s10257-015-0276-5 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Köhling, Christian; Overbeek, Sietse: A Language for Multi-Perspective Goal Modelling: Challenges, Requirements and Solutions. In: Computer Standards & Interfaces (2015), No 38, p. 1-16. doi:10.1016/j.csi.2014.08.001 Details Full textCitation
- Kattenstroth, Heiko; Frank, Ulrich; Heise, David: Towards a Modelling Method in Support of Evaluating Information Systems Integration. In: Jung, Reinhard; Reichert, M. (Ed.): Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Enterprise Modelling and Information Systems Architectures (EMISA ’13), St. Gallen, Schweiz. GI, 2013, p. 85-99. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Multi-Perspective Enterprise Modeling: Foundational Concepts, Prospects and Future Research Challenges. In: Software and Systems Modeling (2013). doi:10.1007/s10270-012-0273-9PDF Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: MEMO Organisation Modelling Language (1): Focus on Organisational Structure - ICB Research Report. 48. Essen, 2011. doi:10.17185/duepublico/47066PDF Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: MEMO Organisation Modelling Language (2): Focus on Business Processes - ICB Research Report. 49. Essen, 2011. doi:10.17185/duepublico/47065PDF Details Full textCitation
- Strecker, Stefan; Heise, David; Frank, Ulrich: RiskM: A multi-perspective modeling method for IT risk assessment. In: Information Systems Frontiers, Vol13 (2011), No 4, p. 595-611. doi:10.1007/s10796-010-9235-3 Details Full textCitation
- Strecker, Stefan; Heise, David; Frank, Ulrich: Toward modeling constructs for audit risk assessment: Reflections on internal controls modeling. In: Esswein, Werner; Turowski, Klaus; Juhrisch, Martin (Ed.): Modellierung betrieblicher Informationssysteme (MobIS 2010) : Modellgestütztes Management, 15.-17. September 2010, Dresden. GI, 2010, p. 131-148. Details Full textCitation
- Heise, David; Heß, Michael; Strecker, Stefan; Frank, Ulrich: Rekonstruktion eines klinischen Behandlungspfads mithilfe domänenspezifischer Erweiterungen einer Geschäftsprozessmodellierungssprache: Anwendungsfall und Sprachkonzepte. In: Thomas, Oliver; Nüttgens, Markus (Ed.): Dienstleistungsmodellierung 2010. Interdisziplinäre Konzepte und Anwendungen. Physica, Heidelberg, 2010, p. 210-227. doi:10.1007/978-3-7908-2621-0_11 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Heise, David; Kattenstroth, Heiko; Ferguson, Donald; Hadar, Ethan; Waschke, Marvin: ITML: A Domain-Specific Modeling Language for Supporting Business Driven IT Management. In: Tolvanen, Juha-Pekka; Rossi, Matti; Gray, J.; Sprinkle, J. (Ed.): Proceedings of the 9th OOPSLA workshop on domain-specific modeling (DSM). Helsinki Business School, Helsinki, 2009. doi:10.1145/1639950.1639975 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Heise, David; Kattenstroth, Heiko: Use of a Domain Specific Modeling Language for Realizing Versatile Dashboards. In: Tolvanen, Juha-Pekka; Rossi, Matti; Gray, J.; Sprinkle, J. (Ed.): Proceedings of the 9th OOPSLA workshop on domain-specific modeling (DSM). Helsinki Business School, Helsinki, 2009. doi:10.1145/1639950.1639975 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Strecker, Stefan: Beyond ERP Systems: An Outline of Self-Referential Enterprise Systems - ICB Research Report. 31. Essen, 2009. doi:10.17185/duepublico/47096PDF Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Heise, David; Kattenstroth, Heiko; Schauer, Hanno: Designing and Utilising Business Indicator Systems within Enterprise Models – Outline of a Method. In: Loos, Peter; Nüttgens, Markus; Turowski, Klaus; Werth, Dirk (Ed.): Modellierung betrieblicher Informationssysteme (MobIS 2008). GI, Bonn, 2008, p. 89-105. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Multiperspektivische Unternehmensmodellierung. In: Kurbel, Karl; Becker, Jörg; Gronau, Norbert; Sinz, Elmar; Suhl, Leena (Ed.): Enzyklopädie der Wirtschaftsinformatik : Online-Lexikon. Oldenbourg, München, 2008. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: The MEMO Meta Modelling Language (MML) and Language Architecture - ICB Research Report. 24. Essen, 2008. doi:10.17185/duepublico/47113PDF Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich; Lange, Carola: E-MEMO: A Method to support the Development of customized Electronic Commerce Systems. In: Information Systems and E-Business Management (ISeB), Vol5 (2007), No 2, p. 93-116. doi:10.1007/s10257-006-0034-9Abstract Details Citation
In many industries structural change through E-Commerce is challenging firms to re-align their strategies as well as re-engineer their business processes with new competitive environments while taking advantage
of technological opportunities. This article presents E-MEMO, a method for multi-perspective enterprise modelling with special emphasis on processes and technologies for E-Commerce. It serves to analyse and design corporate information systems that are balanced with a company’s E-Commerce strategy and its organisation. E-MEMO offers specific languages for modelling strategies, business processes, and related resources. In addition to that, it provides a library of reference models including strategy networks to guide strategic planning and models of business processes. In order to further support the implementation of information systems a transformation has been defined that allows for generating workflow schemata from business process models. Since design-oriented research is not predominant in the Information Systems field, the epistemological challenges of the chosen research approach are discussed, too. - Jung, Jürgen; Kirchner, Lutz: A Framework for Modelling E-Business Resources. 2004. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: E-MEMO: Referenzmodelle zur ökonomischen Realisierung leistungsfähiger Infrastrukturen für Electronic Commerce. In: Wirtschaftsinformatik, Vol46 (2004), No 5, p. 373-381. doi:10.1007/BF03250950 Details Full textCitation
- Jung, Jürgen: Mapping of Business Process Models to Workflow Schemata ‐ An Example Using MEMO-OrgML an XPDL. 2004. Details Full textCitation
- Kirchner, Lutz: Eine Sprache für die Modellierung von IT-Landschaften - Anforderungen, Potenziale, zentrale Konzepte. In: Sinz, E.; Plaha, M.; Neckel, P. (Hrsg) (Ed.): Modellierung betrieblicher Informationssysteme – MobIS 2003, LNI P-38. Köllen Druck+Verlag, Bamberg, 2003, p. 69-86. Citation
- Frank, Ulrich: Multi-Perspective Enterprise Modeling (MEMO): Conceptual Framework and Modeling Languages. In: Sprague Jr., Ralph H. (Ed.): Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS-35): Honolulu. 2002. doi:10.1109/HICSS.2002.993989 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: A Multi-Layer Architecture for Knowledge Management Systems. In: Barnes, Stuart (Ed.): Knowledge Management Systems. Thomson Verlag, 2002, p. 97-111. Details Citation
- Frank, Ulrich; van Laak, Bodo: A Method for the Multi-Perspective Design of Versatile E-Business Systems. In: Ramsower, Regan; Windsor, John (Ed.): Proceedings of the Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2002). 2002. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Multi-Perspective Enterprise Models as a Conceptual Foundation for Knowledge Management. In: Sprague Jr., Ralph H. (Ed.): Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS-33). 2000. doi:10.1109/HICSS.2000.926704 Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Eine Architektur zur Spezifikation von Sprachen und Werkzeugen für die Unternehmensmodellierung. In: Sinz, Elmar (Ed.): Modellierung betrieblicher Informationssysteme: Proceedings der MobIS-Fachtagung 1999. 1999, p. 154-169. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Applying the MEMO-OML: Guidelines and Examples. 1999. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Memo: Visual Languages for Enterprise Modelling. 1999. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: The MEMO Meta-Metamodel. 1998. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: The MEMO Object Modelling Language (MEMO-OML). 1998. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: MEMO: Objektorientierte Unternehmensmodellierung zum gemeinsamen Entwurf optimierter Geschäftsprozesse und hochintegrierter Anwendungssysteme. In: OBJEKTspektrum, Vol1995 (1995), No 6, p. 43-47. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: MEMO: A Tool Supported Methodology for Analyzing and (Re-) Designing Business Information Systems. In: Ege, Raimund; Singh, Madhu; Meyer, Bertrand (Ed.): Technology of Object-Oriented Languages ans Systems. 1994, p. 367-380. Details Full textCitation
- Frank, Ulrich: Multiperspektivische Unternehmensmodellierung als Basis und Gegenstand integrierter CSCW-Systeme. In: Hasenkamp, Ulrich; Kirn, S.; Syring, Michael (Ed.): CSCW-Systeme. 1993, p. 179-198. Details Full textCitation



